Executive Summary: The Dawn of a New Era in Two-Wheeler Mobility
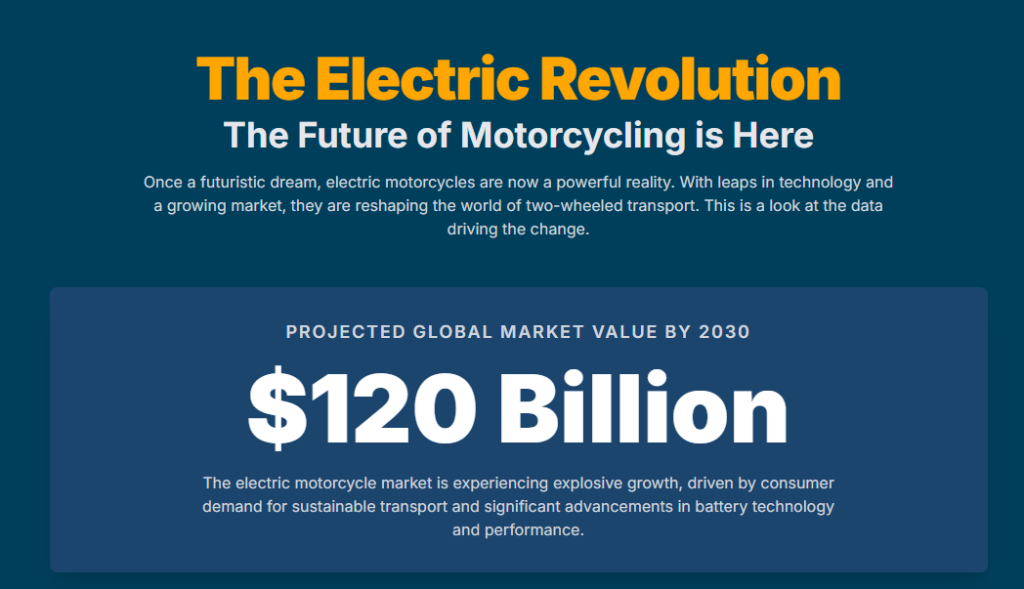
The global electric motorcycle and scooter market is undergoing a significant transformation, evolving from a niche segment into a major force in the automotive industry. A comprehensive analysis of market data, technological advancements, and consumer trends reveals a sector poised for explosive growth and strategic reorientation. The market, valued at approximately USD 37 billion in 2024, is projected to more than double in size, with forecasts ranging from USD 61.73 billion to an ambitious USD 110.6 billion by 2034.1
This remarkable growth is overwhelmingly concentrated in the Asia-Pacific region, which commands over 90% of the market share, led by the dominant influence of China and the rapid emergence of India.1 This dynamic is driven by a powerful confluence of factors: escalating urbanization and traffic congestion, aggressive government incentives, and the strategic collaboration among industry players to manage R&D costs.1
Despite this promising trajectory, significant challenges remain. The high initial purchase price and the considerable long-term cost of battery replacement act as major deterrents for price-sensitive consumers.5 A pervasive “range anxiety” persists, not merely due to limited battery capacity but also because of the lack of a ubiquitous, motorcycle-specific charging infrastructure that supports long-distance travel.5 Furthermore, a cultural disconnect exists for traditional riders who value the visceral experience of a gasoline-powered engine.5
The market is responding to these challenges through an acceleration of technological innovation. Advancements in lithium-ion battery chemistry, the development of next-generation solid-state prototypes, and the integration of sophisticated, AI-driven Battery Management Systems (BMS) are directly addressing performance and durability concerns.2 Concurrently, the competitive landscape is segmenting into two distinct areas: a premium, high-performance segment led by brands like Harley-Davidson’s LiveWire and Zero Motorcycles, and a mass-market, urban commuter segment that dominates in Asian markets.3 This report concludes that while challenges are significant, the convergence of technological progress, supportive policies, and a shift in consumer focus toward urban convenience and sustainability positions the electric motorcycle industry for a quiet revolution in personal mobility.
The Electric Two-Wheeler Market: A Global Perspective
Market Size & Projections (2024-2034)
The electric two-wheeler market, encompassing both motorcycles and scooters, presents a compelling growth narrative for the coming decade. As of 2024, the global market size was valued at USD 36.4 billion according to Global Market Insights and USD 37.93 billion as reported by Precedence Research.1 This marginal variation in the base year valuation is a common occurrence in market analysis, often attributable to differing methodologies and the inclusion or exclusion of specific sub-segments, such as low-speed electric scooters.
Looking forward, the forecasts present a more pronounced divergence, a key point of consideration for stakeholders. Global Market Insights projects a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.1% from 2025 to 2034, leading to a market size of USD 110.6 billion by the end of the forecast period.1 In contrast, Precedence Research provides a more conservative outlook, forecasting a CAGR of 4.99% for the same period, culminating in a market value of approximately USD 61.73 billion by 2034.2
This notable discrepancy in growth rate forecasts is not a simple contradiction but rather represents a fundamental uncertainty regarding the market’s trajectory. The disparity likely stems from differing assumptions about critical variables. A higher growth forecast may presuppose a more aggressive and stable global policy environment, a faster decline in battery costs, and quicker adoption of emerging technologies. Conversely, a more conservative projection may account for potential economic headwinds, policy volatility, and the enduring cultural barriers that currently limit adoption in many key markets. This analysis underscores that the future of the electric two-wheeler market is not preordained but is highly dependent on how these drivers and restraints evolve. The following table visualizes this range of expert opinion on the market’s future.
| Source | Base Year (2024) | Market Size (2024) | Forecast Period | CAGR | Projected Market Size (2034) |
| Global Market Insights | 2024 | USD 36.4 Billion | 2025-2034 | 12.1% | USD 110.6 Billion |
| Precedence Research | 2024 | USD 37.93 Billion | 2025-2034 | 4.99% | USD 61.73 Billion |
Regional Market Dynamics
The global electric two-wheeler market is heavily skewed towards the Asia-Pacific region, which held an overwhelming 90% of the market share in 2024 and accounted for USD 14.5 billion in revenue, driven primarily by China’s colossal market.1 China remains the undisputed dominant player, responsible for 73% of total electric two-wheeler sales in the first half of 2025.4 This market is supported by a high concentration of manufacturers, significant production volumes, and government mandates for electric vehicle quotas.3
India has emerged as the second-largest market and is expected to grow substantially, driven by a combination of new regulations and government incentives such as the FAME III program and the transitional Electric Mobility Promotion Scheme (EMPS) 2024, which allocated over USD 60 billion in subsidies.1 The Southeast Asian market is also showing strong signs of growth, with Vietnam leading the way with nearly 10% electric two-wheeler penetration in sales, followed by Indonesia and the Philippines.1
While smaller in scale, the North American and European markets are experiencing notable expansion. This growth is fueled by increasing environmental awareness, higher disposable incomes, and government support.2 Türkiye, in particular, has become the fastest-growing electric two-wheeler market in Europe, with year-on-year sales exceeding 50,000 units in 2024, bolstered by local manufacturing and VAT exemptions.1
Market Drivers and Strategic Enablers
The transition to electric two-wheelers is being propelled by a series of powerful economic, environmental, and technological forces. These drivers are not isolated but rather work in concert to create a favorable environment for market expansion.
Urbanization and Congestion
The global trend of rapid urbanization has led to a significant increase in urban population density and traffic congestion, which in turn has created a strong market for compact and agile personal transportation. Electric motorcycles and scooters offer a practical and efficient solution for navigating crowded city streets, accessing narrow lanes, and reducing commute times compared to traditional four-wheeled vehicles.2 The small footprint and maneuverability of these vehicles are highly valued by city commuters.
Beyond the practical benefits, electric two-wheelers also address the growing environmental concerns associated with urban living. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, directly combating air pollution in congested areas.2 Furthermore, their quiet operation significantly reduces noise pollution, a critical and often overlooked benefit for both urban residents and wildlife.15 This combination of practicality and environmental stewardship makes electric bikes a compelling and increasingly necessary component of sustainable urban mobility.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government support is a paramount driver of electric vehicle adoption. Policies such as subsidies, tax breaks, and exemptions from registration fees significantly lower the total cost of ownership, thereby accelerating consumer adoption.1 Countries like India, with its FAME III program, and China have successfully used such policies to drive a massive shift towards electric two-wheelers.1 European nations like Norway have even exempted electric motorcycles from tolls and ferry fees, resulting in a remarkable 68% market penetration.10
However, the efficacy of these policies is not without risk. The discontinuation of a major program, such as India’s FAME II on March 31, 2024, which was replaced by a smaller, four-month transitional scheme (EMPS 2024), can create a critical period of market instability.1 A similar reduction in government incentives in Indonesia in December 2024 led to a substantial market loss of 32.2%.4 This dynamic illustrates a critical point: while subsidies can effectively jumpstart a market, their abrupt cessation can lead to market shock and consumer hesitation. A more gradual, long-term approach to policy is essential to foster consumer confidence and enable manufacturers to plan for sustained growth.
Industry Collaboration and Disruption
The transition to electric is a capital-intensive undertaking, characterized by high R&D costs and the need for new supply chains. In response, traditional competitors are increasingly forging strategic partnerships. A clear example is the collaboration between Honda and Yamaha to share development costs and production platforms for small electric motorcycle models targeting Asian and European markets.1 This type of partnership is a fundamental shift in the industry’s competitive dynamic, demonstrating that the financial burden of developing new EV platforms is so immense that collaboration is becoming a more rational strategy than pure competition.
Another strategic approach involves partnerships between legacy brands and specialized electric vehicle companies. The November 2024 partnership between Hero MotoCorp and California-based Zero Motorcycles to develop a mid-sized performance electric motorcycle for the Indian market is a prime example.1 This alliance allows Zero to leverage Hero’s mass-market reach and manufacturing expertise, while Hero gains access to Zero’s advanced high-performance EV technology. These collaborations are not just business news; they signify a fundamental restructuring of the industry to address the economic realities of the electric transition, suggesting that smaller, independent players may struggle to compete on a global scale without similar strategic alliances.
Barriers to Widespread Adoption and Market Restraints
Despite the powerful drivers, several significant obstacles must be overcome for electric two-wheelers to achieve true mass-market dominance outside of a few concentrated regions.
The Cost-Value Equation
For many consumers, the high initial purchase price remains a primary barrier to entry.5 Electric two-wheelers are generally more expensive than their gasoline counterparts with similar performance specifications. This disparity is particularly evident in markets like India, where price sensitivity is high. For instance, the on-road price of a Revolt RV400 in Pune starts at approximately ₹1,40,137, while a comparable Bajaj Pulsar 150 has an ex-showroom price of ₹1,17,229.17 The on-road price of an Ola S1 Pro starts from ₹1,21,342, compared to the TVS Apache RTR 160, which starts at ₹1,18,142.19
This high upfront cost is compounded by the significant expense of battery replacement, which can cost anywhere from ₹40,000 to ₹60,000 and is typically required after 5-6 years.6 While electric bikes offer substantial savings on per-kilometer running costs (e.g., as low as ₹0.13/km for a Revolt RV400 versus ₹2.10/km for a petrol bike), the prospect of a high-cost battery replacement can negate a portion of these long-term savings in the eyes of the consumer.7
Range Anxiety and Infrastructure Gaps
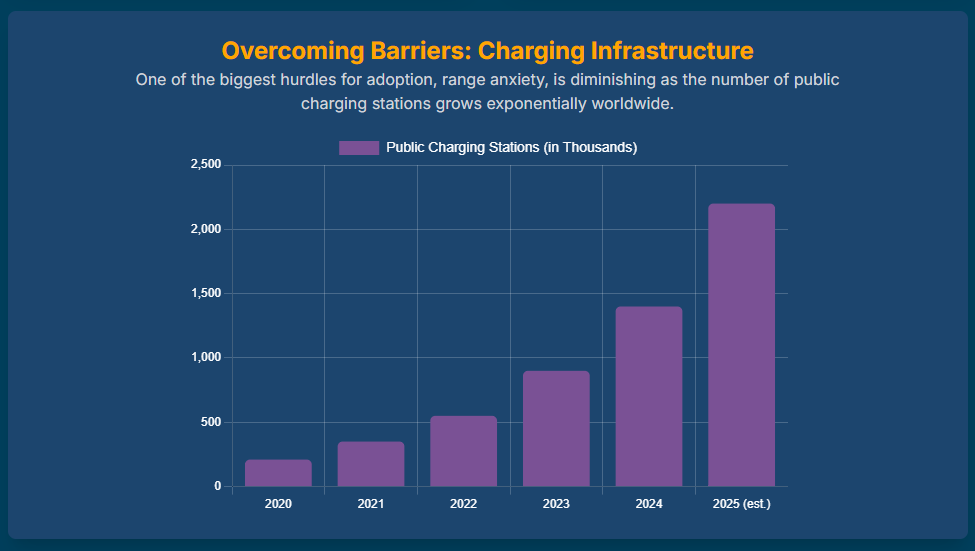
“Range anxiety,” the fear of running out of charge before reaching a destination or a charging station, is a major impediment to adoption, especially for riders who need to travel long distances.5 The practical limitations of battery size on a motorcycle often result in a range that falls short of what gasoline riders are accustomed to, a critical factor for long-distance touring.5
This issue is exacerbated by the current charging infrastructure. While an increasing number of charging stations are being established in cities like Pune 23, the mere existence of these stations does not fully solve the problem for motorcycle riders. Public charging stations are often designed for electric cars, which have different space and charging speed requirements. Motorcycle riders need fast-charging options that do not require them to leave their vehicle for hours.5 The paradoxical nature of this challenge is that a growing number of chargers are being deployed, yet the network is not yet optimized for the specific use cases of electric two-wheelers. For example, a LiveWire One supports DC fast charging, but the newer S2 platform does not, highlighting product-specific incompatibilities.25 This reveals that the
type, location, and compatibility of charging stations are more crucial than their sheer number, suggesting that a focus on motorcycle-specific infrastructure, such as battery swapping networks, is a necessary next step.5
Cultural and Emotional Barriers
For many enthusiasts, riding a motorcycle is more than a mode of transport; it is a lifestyle, a cultural expression, and a community built around the unique sensory experience of a gasoline engine.5 The loud, raw sound of a combustion engine, the vibrations, and the manual control of a clutch and gears are all central to the experience for many riders.5 The silent and smooth operation of electric motorcycles, while a benefit for urban environments, can be a significant cultural disconnect for these traditional riders.15 This intangible barrier, rooted in decades of association with combustion engines, is perhaps the most difficult for the industry to overcome.11 While manufacturers are attempting to address this by highlighting the thrill of instant torque and unprecedented acceleration, it remains a powerful headwind, particularly in markets with a strong, established motorcycle culture.8
Technological Innovations: The Engine of Progress
The future of the electric two-wheeler market is inextricably linked to the rapid pace of technological evolution, with innovations in battery technology and integrated software systems serving as the primary drivers of progress.
Battery Technology
The core of any electric vehicle is its battery, and significant strides are being made to enhance energy density, charging speed, and durability.
Lithium-Ion Evolution
Modern lithium-ion batteries are achieving a 20-30% higher energy density compared to 2020 models through the use of nickel-rich cathodes and the integration of silicon-anodes.9 This enables longer ranges without increasing the physical size or weight of the battery pack.3 Manufacturers like Zero Motorcycles are also employing specialized cell configurations and advanced thermal management systems to ensure durability, with some batteries maintaining 80% capacity after 1,500 charge cycles, even in extreme temperatures ranging from -20°C to 60°C.9
Solid-State and Graphene
Looking to the future, solid-state and graphene-enhanced batteries hold the promise of revolutionizing the industry. Solid-state prototypes for motorcycles have demonstrated an energy density of 400 Wh/kg, which is double that of current lithium-ion batteries.9 These batteries also offer enhanced safety by eliminating flammable liquid electrolytes.9 Test models from Honda have shown the ability to achieve a 0-80% charge in just 15 minutes using ceramic-based electrolytes.9 Similarly, graphene-enhanced batteries, currently in pilot production, offer the potential for 3-minute fast charging and a 50% reduction in battery weight, paving the way for 1,000 km ranges.9 While the commercialization of these technologies faces challenges related to high production costs and manufacturing scalability, their development signifies the enormous potential for future performance breakthroughs.
The most critical innovation in battery technology is not just in the chemistry itself but in the intelligent software that manages it. Modern Battery Management Systems (BMS) are becoming increasingly sophisticated, leveraging machine learning algorithms to predict cell failures with up to 92% accuracy.9 These systems automatically balance the charge across individual cells in real time, which can extend the lifespan of a battery pack by as much as 40%.9 Some models, such as Harley-Davidson’s latest offerings, even feature a GPS-linked BMS that preheats the battery as the rider approaches a charging station to optimize charge acceptance rates.9 This trend illustrates that manufacturers are now competing not just on hardware specifications but on the intelligence and sophistication of their software and data-driven systems.
Advanced Safety and Connectivity
Modern electric motorcycles are moving beyond basic transportation to become integrated, rolling data platforms. The integration of advanced features is enhancing safety, convenience, and the overall user experience. High-end models are increasingly incorporating advanced rider-assistance systems (ADAS), which use a 360-degree scan of the surroundings to alert riders of potential dangers through haptic handlebar feedback, integrated windscreen LEDs, and always-operational cameras and long-range radar.8 This level of built-in safety technology far surpasses what is typically available in gasoline motorcycles.8
Connectivity is also becoming a standard feature. Many models include over-the-air (OTA) updates for software and firmware, ensuring the bike remains current with the latest features and optimizations.26 Connected apps provide real-time data on battery status, ride statistics, and location tracking.25 These systems not only enhance the user experience but also provide manufacturers with a stream of aggregated, anonymous data that can be used to improve future models, offer new services, and optimize the overall ecosystem. This trend signifies a shift toward a new business model where long-term value is tied not just to the vehicle but to the data ecosystem it creates.8
Competitive and Product Landscape Analysis
The electric two-wheeler market’s competitive landscape is dynamic and multifaceted, with a clear separation emerging between high-performance premium models and mass-market commuters.
Major Players and Strategic Positioning
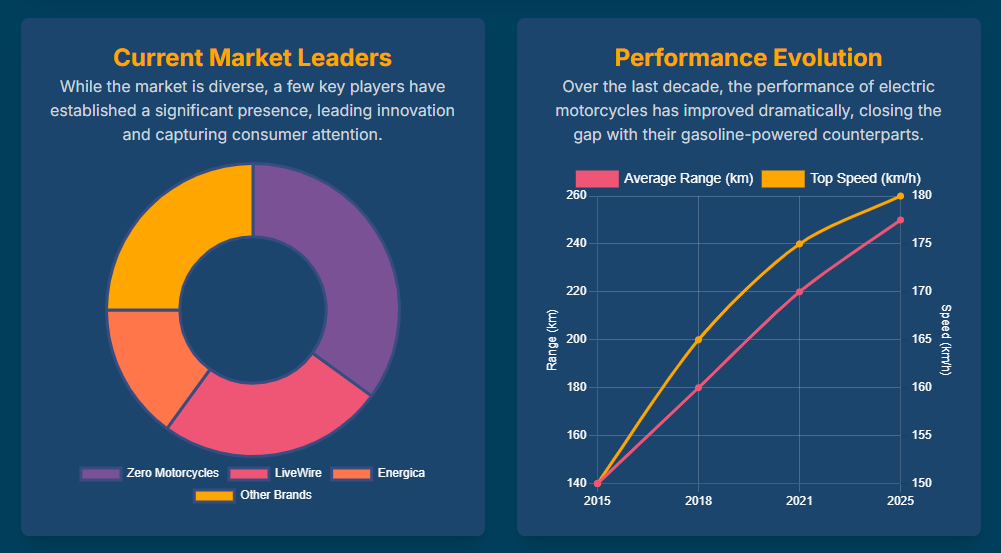
The market is led by a mix of traditional and specialized brands. Harley-Davidson, through its LiveWire brand, has strategically positioned itself to expand beyond its traditional cruiser format to tap into the urban mobility market with products like the electric maxi-scooter.1 Zero Motorcycles maintains its leadership in the recreational and enthusiast segments, offering a range of high-performance bikes like the SR/F and DSR/X.1 Meanwhile, Chinese giants like Yadea dominate the mass-market and scooter segments, holding a significant portion of the market share.1 The entry of legacy manufacturers like Honda, Kawasaki, and Royal Enfield, with their deep pockets and extensive distribution networks, signals a major shift.1
Deep Dive: Performance vs. Commuter Models
Performance Segment
The premium segment is defined by a focus on high-performance metrics and advanced features. The LiveWire S2 Del Mar, for example, is a performance-oriented bike with a claimed 84 hp and 194 lb-ft of torque, capable of a 0-60 mph acceleration in 3 seconds.26 It features a 10.5 kWh battery and high-end components such as Showa suspension and Brembo brakes.26 In comparison, the Zero SR/F offers a higher claimed horsepower of 110 hp and 140 ft-lbs of torque, with a larger 14.4+ kWh battery.12 This focus on performance metrics is a direct response to the cultural barrier of appealing to traditional riders, as it highlights the thrill of instant torque and rapid acceleration that can even surpass that of many gasoline bikes.8
Urban Commuter Segment (Case Study: India)
The Indian market is a powerful illustration of the commuter segment’s growth. Popular models like the Ola S1 Pro, Revolt RV400, and Ultraviolette F77 compete fiercely on price, features, and claimed range.31 The Ola S1 Pro has a claimed range of 176 km with a top speed of 117 kmph, while the Revolt RV400 offers a claimed range of 150 km and a top speed of 85 kmph.33 The Ultraviolette F77 Mach 2 Recon, a premium offering in the Indian market, boasts a claimed range of 323 km and a top speed of 155 kmph.27 On-road prices for these models can vary significantly, starting at ₹1,40,137 for the Revolt RV400 and ranging up to ₹4,62,999 for the Ultraviolette F77 Mach 2 Recon in Pune, with prices heavily influenced by subsidies and RTO charges.17
The following tables provide a direct comparison of key specifications and the total cost of ownership, illustrating the trade-offs and value propositions in both the performance and commuter segments.
| Model | Target Segment | Power (hp/kW) | Torque (lb-ft/Nm) | 0-60 mph | Battery Capacity (kWh) | Claimed Range | Curb Weight (lb/kg) | Charging Time (L2) |
| Zero SR/F | Performance | 110 hp / — | 140 lb-ft / 190 Nm | 3 sec | 14.4+ kWh | 171-179 mi | 518 lb / 235 kg | 1 hour (with charge-tank) 12 |
| LiveWire S2 Del Mar | Performance | 84 hp / 63 kW | 194 lb-ft / 263 Nm | 3 sec | 10.5 kWh | 113 mi (City) | 436 lb / 198 kg | 78 min (20-80%) 25 |
| LiveWire One | Performance | 100 hp / 75 kW | 84 lb-ft / 114 Nm | 3 sec | 15.4 kWh | 146 mi (City) | 562 lb / 255 kg | 40 min (0-80% DCFC) 37 |
| Can-Am Origin | Dual Sport | — | — | — | 8.9 kWh | — | — | — |
| Ultraviolette F77 | Urban Sport | 30 kW / 40.8 hp | 100 Nm / 74 lb-ft | 7.7 s (0-100 kph) | 10.3 kWh | 323 km / 200 mi | 197 kg / 434 lb | 2.5 hr (20-80% Boost) 27 |
| Item | Ola S1 Pro (EV) | Revolt RV400 (EV) | TVS Apache RTR 160 (ICE) | Bajaj Pulsar 150 (ICE) |
| Initial On-Road Price in Pune | ₹1,21,342-₹1,41,699 19 | ₹1,40,137-₹1,47,258 17 | ₹1,18,142 20 | ₹1,17,229-₹1,42,934 18 |
| Running Cost per km | ₹0.17 20 | ₹0.13-₹0.22 7 | ₹2.27 20 | ₹2.11-₹2.13 18 |
| Est. Annual Maintenance | ₹500-₹1,500 7 | ₹500-₹1,500 7 | ₹3,000-₹6,000 7 | ₹3,000-₹6,000 7 |
| Battery Replacement Cost | ₹65,000 (after 3.5 years) 21 | ₹50,000-₹60,000 (after 6-8 years) 7 | N/A | N/A |
Strategic Outlook and Future Projections
The electric motorcycle market stands at a pivotal inflection point, with a clear trajectory toward a bifurcated structure. The market is expected to solidify into two primary segments: a high-performance, premium segment catering to enthusiasts and a mass-market, last-mile delivery segment focused on urban convenience and low operational costs.10
Mass adoption appears inevitable as key technological and economic barriers are systematically dismantled. The cost of batteries is a critical factor, and industry analysts predict that as these costs drop below the USD 75/kWh threshold and technological advancements like solid-state batteries and AI become standard, the value proposition for consumers will become too compelling to ignore.10 The rise of the shared economy and last-mile logistics is also poised to drive significant fleet adoption, with forecasts suggesting that 40% of all food delivery fleets in megacities will be electric by 2027.10
Recommendations for Stakeholders
To capitalize on this transformative period, stakeholders must adopt targeted strategies.
- For Manufacturers: The high costs and rapid pace of technological change necessitate a shift in strategy. Manufacturers should focus on developing modular platforms that can be adapted for multiple models to reduce R&D costs.10 The competitive edge will increasingly come from investments in smarter software and data-driven systems, particularly in Battery Management Systems that can optimize performance and extend battery lifespan.9 Exploring alternative ownership models, such as battery-as-a-service or leasing, could also mitigate the high upfront costs and long-term battery replacement anxiety for consumers.7
- For Governments: Stable, long-term policy is essential to foster market confidence and investment. Governments should implement predictable, phased-out incentive programs rather than relying on temporary schemes that can cause market shock.4 Supporting the development of a universal charging infrastructure is also critical, with a focus on establishing charging standards like AIS-138 and ensuring the network is tailored to the specific needs of motorcyclists, including the provision of fast-charging and battery swapping stations.40
- For Consumers: Potential buyers should look beyond the initial purchase price and consider the total cost of ownership over the vehicle’s lifespan, accounting for significant savings on fuel and maintenance, as well as the eventual cost of battery replacement.6 The reputation of a manufacturer’s service network and its commitment to software updates is also a critical factor for long-term satisfaction and reliability.21
Final Thoughts
The electric motorcycle market is at a critical juncture. While a number of significant barriers remain, particularly those related to initial cost and infrastructure, the industry’s response has been one of robust innovation and strategic adaptation. The convergence of technological breakthroughs in battery chemistry and AI, combined with the tailwinds of urbanization and supportive government policies, is propelling the industry forward. The market is no longer a futuristic concept but a practical reality that is reshaping urban mobility and personal transportation, setting the stage for not just an evolution, but a quiet revolution.
Sources
- Electric Motorcycle & Scooters Market Size, Forecasts 2025-2034, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/electric-motorcycles-and-scooters-market
- Electric Motorcycle and Scooters Market Size to Worth USD 61.73 Bn by 2034, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.precedenceresearch.com/electric-motorcycle-and-scooters-market
- Future-Ready Strategies for Electric Motorcycle Market Growth, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.datainsightsmarket.com/reports/electric-motorcycle-130844
- Electric Motorcycles Market 2025 – Data & Facts | MotorCyclesData, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.motorcyclesdata.com/2025/08/05/electric-motorcycles-market/
- Why Electric Motorcycles are Failing | My EV Discussion, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://myevdiscussion.com/threads/why-electric-motorcycles-are-failing.625/
- Electric vs. Petrol Motorcycles: Pros and Cons You Must Know – neodrift, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.neodrift.in/blogs/neodrifts-guide/electric-vs-petrol-motorcycles-pros-and-cons-you-must-know
- Real Running Cost of Electric Bikes in India 2025 Explained – Revolt Motors, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.revoltmotors.com/blog/real-running-cost-of-electric-bike-in-india
- Electric Motorcycles Vs. Gas Motorcycles – Damon Motorcycles, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://damon.com/blog/electric-motorcycle-vs-gas-motorcycle/
- What Are The Latest Electric Motorcycle Battery Advances?, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.happyrunsports.com/blogs/news/what-are-the-latest-electric-motorcycle-battery-advances
- What Are the Future Trends in Electric Motorcycles? – HappyRun, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://happyrunsports.com/blogs/electric-motorcycle/what-are-the-future-trends-in-electric-motorcycles
- Electric Motorcycle Guide (2025) – Is the future really electric? – Bennetts Insurance, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bennetts.co.uk/bikesocial/news-and-views/features/electric-motorcycles/guide
- 10 New Electric Motorcycles That Turn Heads In 2025 – Top Speed, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.topspeed.com/new-electric-motorcycles-that-turn-heads-2025/
- www.happyrunsports.com, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.happyrunsports.com/blogs/electric-motorcycle/what-environmental-benefits-come-from-owning-an-electric-motorcycle#:~:text=Electric%20motorcycles%20produce%20zero%20direct,this%20footprint%20to%20near%20zero.
- 5 Reasons Electric Motorcycles are an Eco-Friendly Choice for City Commuters, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://urbanbikesdirect.com/blogs/news/5-reasons-electric-motorcycles-are-an-eco-friendly-choice-for-city-commuters
- Why Electric Motorcycles Can Be Better Than Gas Motorcycles | Sky Powersports Sanford, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.skypowersportssanford.com/blog/why-electric-motorcycles-can-be-better-than-gas-motorcycles/
- Government Subsidy for Electric Bikes in India: A Complete 2025 Guide – Revolt Motors, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.revoltmotors.com/blog/government-subsidy-for-electric-bikes-in-india
- August 2025 on road price of RV400 in Pune – Revolt – BikeWale, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikewale.com/revolt-bikes/rv400/price-in-pune/
- Bajaj Pulsar 150 vs Revolt RV400 – Know Which Is Better! – BikeWale, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikewale.com/compare-bikes/bajaj-pulsar-150-vs-revolt-rv400/
- S1 Pro On Road Price in Pune – Ola Electric Scooters – BikeDekho, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikedekho.com/ola-electric/s1-pro/price-in-pune
- OLA S1 Pro vs TVS Apache RTR 160 – Know Which Is Better! – BikeWale, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikewale.com/compare-bikes/ola-s1-pro-vs-tvs-apache-160/
- Reviews of OLA S1 Pro – BikeWale, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikewale.com/ola-bikes/s1-pro/reviews/
- River Indie Price – Range, Images, Colours – BikeWale, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikewale.com/river-bikes/indie/
- List Of EV Charging Station in Pune | 123ElectricVehicles, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.123electricvehicles.com/ev-charging-stations/pune
- Electric Vehicle Charging Station – Pune Municipal Corporation, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.pmc.gov.in/en/project/electric-vehicle-charging-station
- Electric motorcycle charging 101 | LiveWire, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.livewire.com/the-pulse/learn/electric-motorcycle-charging-101
- S2 Del Mar Launch Edition | LiveWire United States, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.livewire.com/s2-del-mar-launch-edition
- Ultraviolette F77 Price, Mileage, Range, Charging Time – BikeDekho, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikedekho.com/ultraviolette/f77
- Zero SR/F – Electric Motorcycle – Moto Z, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.motoz.net/zero-sr-f
- TVS iQube, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://tvsnepal.com/iqube/faq
- Here Are Your Full LiveWire S2 Del Mar Specifications In Detail – RideApart.com, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.rideapart.com/news/677322/livewire-s2-del-mar-specs/
- Best Electric Bikes 2025, Electric Vehicles Charging Stations, Charging Bikes – BikeDekho, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikedekho.com/electric-zone
- Electric Bike Price, Battery Bikes, Images, Reviews – BikeDekho, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikedekho.com/electric-bikes
- Ola S1 Pro Specifications, Features, Mileage, Weight, Tyre Size – BikeDekho, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikedekho.com/ola-electric/s1-pro/specifications
- Revolt RV400 Price, Mileage, Range, Weight – BikeDekho, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikedekho.com/revolt/rv-400
- Ultraviolette F77 Price in Pune (On Road) – BikeDekho, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikedekho.com/ultraviolette/f77/price-in-pune
- Electric Motorcycle Chargers Explained – Australian Electric Motor Co, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://australianelectricmotorco.com/how-to-guides/electric-motorcycle-chargers-explained/
- Best Electric Motorcycles of 2025 – Motorcyclist, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.motorcyclistonline.com/news/best-electric-motorcycles/
- Ultraviolette : High-Performance Electric Vehicles, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.ultraviolette.com/f77
- Bajaj Pulsar 150 vs Revolt RV400 – Compare Prices, Specs, Features – ZigWheels.com, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.zigwheels.com/bike-comparison/bajaj-pulsar-150-vs-revolt-rv-400
- Arai Standard – e-AMRIT, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://e-amrit.niti.gov.in/arai-standard
- for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://mohua.gov.in/upload/whatsnew/5c6e472b20d0aGuidelines%20(EVCI).pdf
- OLA S1 Pro vs TVS Apache RTR 160 4V – Know Which Is Better! – BikeWale, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikewale.com/compare-bikes/ola-s1-pro-vs-tvs-apache-rtr-160-4v/
- Reviews of Revolt RV400 – BikeWale, accessed on August 30, 2025, https://www.bikewale.com/revolt-bikes/rv400/reviews/
Our Social Media Handles
- Instagram : LivingWithGravity
- Medium : Akash Dolas
- YouTube Channel : Gear and Shutter
- Facebook : LivingWithGravity