Key Points
- Yamaha is taking a multifaceted approach to finding alternatives to the gasoline internal combustion engine.
- Hydrogen fuel is one possibility Yamaha is exploring.
- Hydrogen fuel cells are more efficient than traditional gasoline engines and produce zero emissions.
- The technology is not yet as widespread as electric vehicles, and some challenges remain, such as the cost of hydrogen fuel and the lack of refuelling infrastructure.
- Yamaha is confident hydrogen fuel has the potential to be a major player in the future of mobility.
- Yamaha is not the only company exploring the potential of hydrogen fuel. Other major automakers, such as Toyota and Honda, also invest in hydrogen fuel cell technology.
- As technology develops, we will likely see more hydrogen-powered vehicles on the road.
- It is still too early to say whether hydrogen fuel will become the dominant fuel of the future. However, Yamaha’s commitment to hydrogen fuel shows the company is taking the future of mobility seriously. By exploring various possibilities, Yamaha is positioning itself to be a leader in developing new mobility technologies.

Future
While it is widely acknowledged electric power is a major part of the future for the automotive and motorcycle industries, Yamaha believes in keeping an open mind and exploring various possibilities. In addition to its intensive efforts in electric powertrains and battery technology, Yamaha is also developing an e-fuel program and considering hydrogen as an alternative.
Yamaha’s CEO
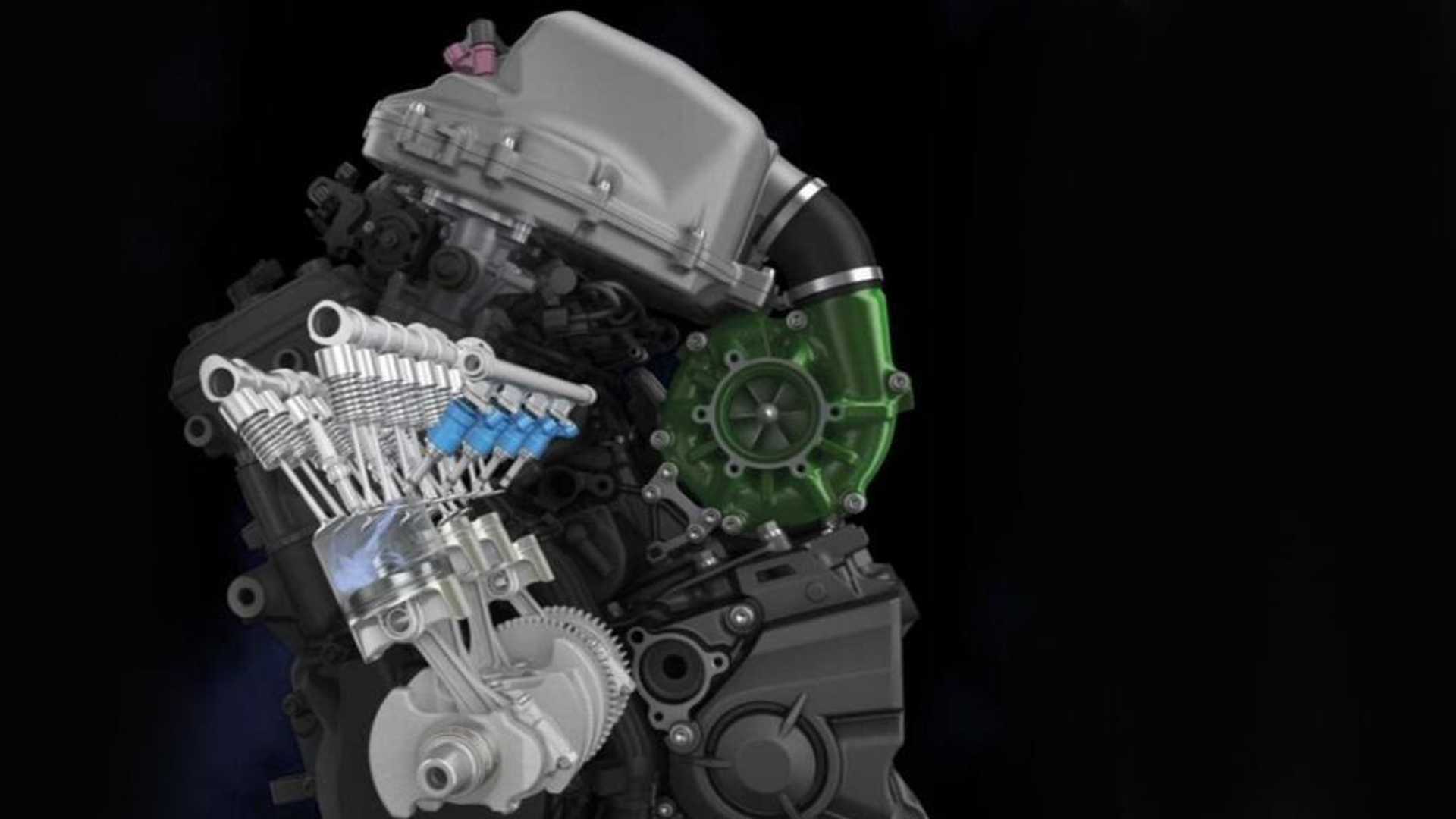
Yamaha’s CEO, Yoshihirro Hidaka, stated the company aims to maintain multiple possibilities to achieve carbon neutrality. Yamaha recognizes the existence of hydrogen electric vehicles, such as the Toyota Mirai, but it focuses on preserving the internal combustion engine by using hydrogen power. The company has experience in hydrogen-powered combustion engines through its collaboration with Toyota on the world’s first liquid-cooled hydrogen race car.
While hydrogen fuel holds potential, it currently has drawbacks. It is less fuel-efficient than traditional gasoline, and the hydrogen refuelling infrastructure is not as widespread as electric charging infrastructure. Electric vehicles were also considered niche technology at one point and have gained rapid adoption in recent years.
Mobility
With Yamaha being a key player in the automotive and motorcycle industries, along with the broader influence of Japan’s automotive sector, they have the potential to shape the future of mobility. Yamaha believes in having the technology ready and archived, so they can bring the technology to market and begin mass development when the world moves in a particular direction.
Here are some pros and cons of exploring hydrogen power as an alternative in the automotive and motorcycle industries:
Pros of Hydrogen Power:
- Environmental Benefits: Hydrogen is a clean fuel source, as it produces only water vapour when used in fuel cells or burned in combustion engines. It can potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to overall environmental sustainability.
- Quick Refueling: Hydrogen-powered vehicles can be refuelled quickly, similar to conventional gasoline vehicles. This can provide convenience and eliminate the longer charging times associated with electric vehicles.
- Longer Range: Hydrogen-powered vehicles typically have a longer range than electric vehicles, allowing extended travel without frequent refuelling.
- Familiar Driving Experience: Unlike electric vehicles, hydrogen-powered vehicles can retain the familiar driving experience of internal combustion engines, which may appeal to consumers accustomed to traditional vehicles.
Cons of Hydrogen Power:
- Limited Infrastructure: The infrastructure for producing, distributing, and refuelling hydrogen is limited compared to electric charging infrastructure. Hydrogen refuelling stations are not as widely available, which can pose challenges for potential hydrogen vehicle owners.
- Energy Efficiency: The production and storage of hydrogen can be energy-intensive, leading to lower overall energy efficiency than electric vehicles. This means more energy is needed to produce a given amount of usable energy from hydrogen fuel.
- Cost: Hydrogen production and infrastructure development can be costly. The initial investment required for building hydrogen refuelling stations and establishing a hydrogen supply chain can be significant, affecting the affordability and accessibility of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
- Safety Concerns: Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires careful handling and storage. Ensuring the safety of hydrogen-powered vehicles and infrastructure is a critical consideration.
- Technology Maturity: While hydrogen-powered vehicles have been developed and produced, the technology is still considered relatively new and less mature than electric vehicles. This may result in ongoing research, development, and improvements to enhance efficiency, safety, and overall performance.
Conclusion
Exploring hydrogen power as an alternative in the automotive and motorcycle industries presents advantages and challenges. On the positive side, hydrogen offers environmental benefits, quick refuelling, longer range, and a familiar driving experience. However, limitations include limited infrastructure, lower energy efficiency, cost considerations, safety concerns, and the technology’s relative immaturity compared to electric vehicles.
Ultimately, the viability of hydrogen power will depend on factors like the development of hydrogen infrastructure, technological advancements, government support, and consumer acceptance.
While electric power is currently dominant in the industry, Yamaha’s open-minded approach and exploration of various alternatives, including hydrogen, demonstrate a commitment to finding sustainable solutions for the future. As the industry continues to evolve, it remains to be seen which technologies will prevail and shape the future of mobility.