I. Executive Summary
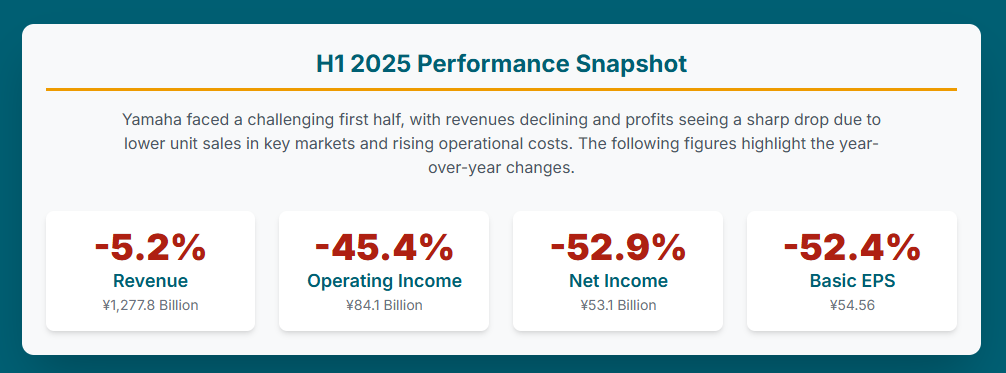
Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. experienced a challenging first half of fiscal year 2025, marked by a significant downturn in both revenue and profitability. For the six months ended June 30, consolidated revenue stood at ¥1,277.8 billion (approximately $8.63 billion USD), representing a 5.2% decrease compared to the same period in the previous year.1 This top-line decline was accompanied by a much sharper erosion of profits: operating income plummeted by 45.4% to ¥84.1 billion (approximately $568 million USD), while net income attributable to owners of parent fell by 52.9% to ¥53.1 billion (approximately $359 million USD).3 Profit before tax also saw a substantial decrease of 46.2% to ¥82.920 billion.8 Consequently, basic earnings per share (EPS) nearly halved, dropping to ¥54.56 from ¥114.60 in the prior year.8
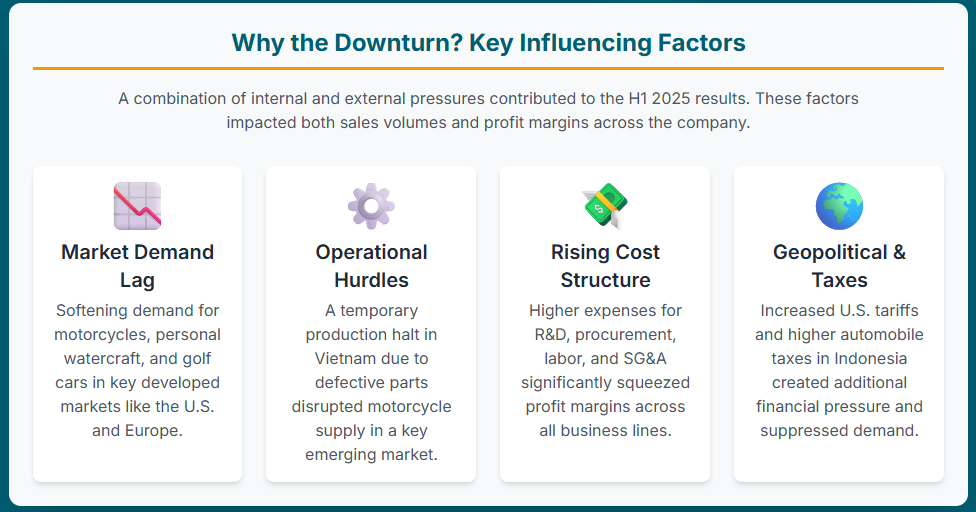
The primary factors contributing to this downturn include lower unit sales across key product lines such as motorcycles, personal watercraft, and golf cars, particularly in developed markets like the U.S. and Europe, and emerging markets like India and Brazil.3 Operational disruptions, such as a temporary suspension of motorcycle production in Vietnam due to defective engine stamping, further exacerbated sales declines.1 Concurrently, profitability was severely impacted by higher research and development (R&D) expenses, elevated procurement costs, and increased labor and other selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses.1 External headwinds, including increased U.S. tariffs and higher automobile taxes in Indonesia, also weighed on performance and the future outlook.1
Despite these challenging conditions, Yamaha Motor demonstrated resilience by gaining market share in some key areas within its core businesses, including motorcycles and marine products.5 The company also highlighted positive performance in its Robotics business, which saw significant revenue growth driven by demand for generative AI applications and advanced packaging.10 Strategic R&D investments continue, focusing on areas like cell handling technology and electric/hybrid products, signaling a long-term commitment to innovation and diversification.13
Reflecting the challenging first-half performance and anticipated persistent headwinds, Yamaha Motor significantly revised its full-year 2025 financial forecasts downwards. The company now projects attributable profit to be ¥45.0 billion, a drastic cut from the initial expectation of ¥140.0 billion.9 This revised outlook suggests a more cautious approach, yet management remains committed to implementing thorough cost controls and improving its profit structure while maintaining its dividend forecast.5
II. Introduction
Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. is a globally recognized leader in the manufacturing of a diverse range of products, including motorcycles, marine products, power products, and industrial machinery. With a long-standing reputation for innovation, quality, and performance, Yamaha has established a significant presence across various sectors, from powersports and recreational vehicles to advanced robotics and financial services. The company’s strategic positioning aims to deliver “Kando” – a Japanese word for the simultaneous feeling of deep satisfaction and intense excitement – through its products and services worldwide.
This report aims to provide an exhaustive, insightful, and nuanced analysis of Yamaha Motor’s financial performance for the first half of fiscal year 2025. It delves into the underlying drivers of the reported declines, examines the strategic implications for the company’s future trajectory, and explores the broader market context. The analysis encompasses segmental and regional dynamics, a detailed review of cost pressures, the nature and impact of R&D investments, and a synthesis of market sentiment regarding the company’s outlook.
The information presented in this report synthesizes data from official company financial releases, including consolidated business results summaries and investor relations documents, as well as reports from reputable news agencies and financial analysis platforms. The focus is specifically on the first half of fiscal year 2025, covering the period from January 1 to June 30, 2025. Currency conversions from Japanese Yen (¥) to U.S. Dollars ($) are based on the reported average exchange rates for the first half-year consolidated accounting period, where the U.S. dollar traded at ¥148 and the euro at ¥162.1
III. H1 2025 Consolidated Financial Performance: A Detailed Review
Yamaha Motor’s consolidated financial results for the first half of 2025 reveal a significant contraction in both revenue generation and profitability. This performance reflects a challenging global economic environment coupled with specific operational and market-related pressures.
Revenue Analysis: Trends and Year-over-Year Changes
For the six months ended June 30, 2025, Yamaha Motor reported consolidated revenue of ¥1,277.8 billion, which translates to approximately $8.63 billion USD. This figure represents a 5.2% decrease compared to the ¥1,348.443 billion recorded in the same period of the previous fiscal year.1 This decline in top-line performance can be attributed to lower unit sales across several key product categories, including motorcycles, personal watercraft, and golf cars, as well as broader cooling of demand in key powersports markets globally.1
Profitability Metrics: Operating Income, Net Income, and Profit Before Tax
The impact on profitability was considerably more severe than the revenue decline. Operating income for the first half of 2025 was ¥84.1 billion (approximately $568 million USD), marking a sharp 45.4% decrease from ¥154.055 billion in the prior year.1 Net income attributable to owners of parent experienced an even steeper decline, falling by 52.9% to ¥53.1 billion (approximately $359 million USD) from ¥112.858 billion in the comparable period.3 Profit before tax also decreased significantly by 46.2% to ¥82.920 billion from ¥154.109 billion.8
The disparity between the modest revenue decline and the drastic drops in operating and net income indicates a severe compression of profit margins for Yamaha in the first half of 2025. This suggests that the company’s challenges extended beyond a mere reduction in sales volume to encompass a more fundamental issue with its cost structure and pricing power. A significant portion of the company’s costs, such as R&D expenses and labor costs, tend to be fixed or less flexible in the short term. When revenue declines, these fixed costs can disproportionately impact profitability, leading to a magnified reduction in the bottom line. Furthermore, increased variable costs, including higher procurement expenses, directly reduce the gross profit margin. The company’s statements explicitly cite higher procurement expenses, increased R&D expenses, and elevated labor and other SG&A expenses as key contributors to the decrease in profits.1 An unfavorable shift in the product mix, where sales might have tilted towards lower-margin products, as hinted by the “worsening model mix” in recreational vehicles, could also have played a role in eroding overall profitability.10 The combined effect of these factors resulted in a challenging cost environment that eroded profitability far more severely than the top-line revenue decline might initially suggest.
Earnings Per Share (EPS) Performance
Reflecting the sharp decline in net income, basic earnings per share (EPS) for H1 2025 fell to ¥54.56, a substantial decrease from ¥114.60 per share in the same period a year ago.8
Impact of Foreign Exchange Fluctuations
For the first half-year consolidated accounting period, the U.S. dollar traded at an average of ¥148, representing an increase of ¥4 from the same period of the previous fiscal year. The euro similarly strengthened against the yen, trading at ¥162, an increase of ¥3.1 While a weaker yen generally benefits Japanese exporters by making their products more competitive abroad and increasing the yen value of overseas earnings, the overall financial results indicate that other negative factors, such as declining unit sales and rising costs, outweighed any potential positive currency translation effects.
Table 1: Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. Consolidated Financial Highlights (H1 2025 vs. H1 2024)
| Metric | H1 2025 (¥ Billion) | H1 2025 (USD Million/Billion) | H1 2024 (¥ Billion) | YoY Change (%) |
| Revenue | 1,277.8 | $8.63 Billion | 1,348.443 | -5.2% |
| Operating Income | 84.1 | $568 Million | 154.055 | -45.4% |
| Net Income | 53.1 | $359 Million | 112.858 | -52.9% |
| Profit Before Tax | 82.920 | N/A | 154.109 | -46.2% |
| Basic EPS (¥) | 54.56 | N/A | 114.60 | -52.4% |
Note: USD conversions are approximate based on average exchange rates for H1 2025 where $1 = ¥148 and €1 = ¥162. Some USD figures are directly provided by sources.
IV. Segmental Performance Analysis
Yamaha Motor’s diverse business portfolio experienced varied performance across its segments, with some facing significant headwinds while others demonstrated resilience and growth.
A. Land Mobility Business
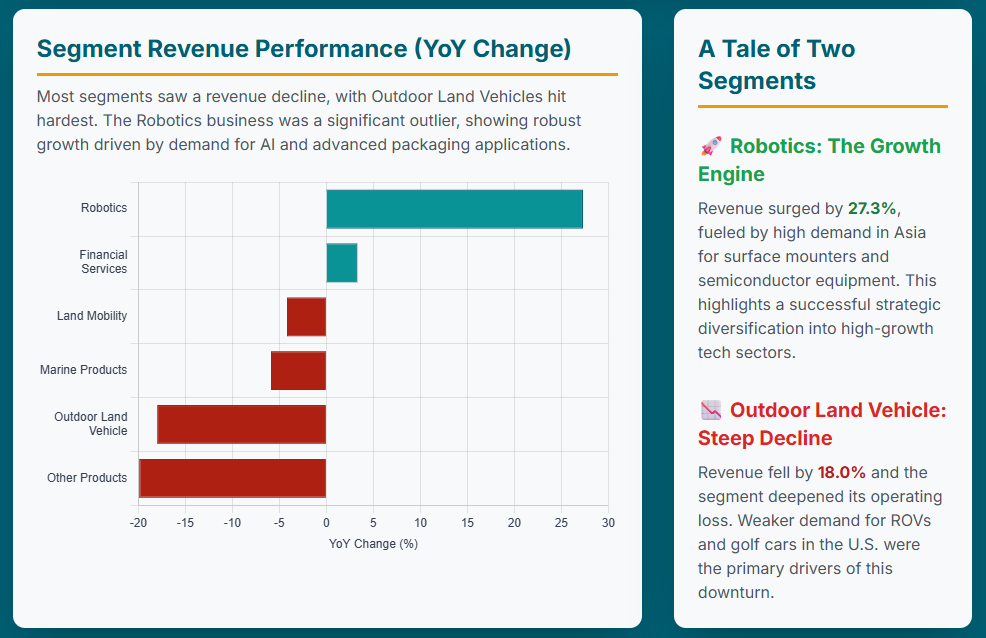
The Land Mobility segment, encompassing motorcycles, scooters, and e-bikes, reported revenues of ¥808.2 billion (approximately $5.46 billion USD) for the first half of 2025, a decrease of 4.2% year-over-year. Operating income for this segment fell by a substantial 39.0% to ¥59.4 billion (approximately $401 million USD).3
Within the motorcycle business, unit sales in developed markets, particularly Europe and the U.S., declined due to softening demand.3 However, sales in Japan showed an increase, which helped to partially offset the declines and bring overall revenue for the region closer to the previous year’s level.5 In emerging markets, overall unit sales decreased compared to the prior year. This was largely driven by a temporary suspension of production and shipments in Vietnam during the first quarter, triggered by issues such as defective engine stamping.1 Additionally, lower unit sales were recorded in India and Brazil, with India experiencing a significant 17.4% decline in a highly competitive market.5 The operational vulnerability highlighted by the Vietnam production halt, stemming from an internal quality control issue rather than just market demand, underscores a critical area for improvement within Yamaha’s manufacturing processes. The challenges in India also suggest a need for more agile product updates, especially in the burgeoning electric scooter segment where Yamaha’s current offerings may not be as competitive.11 The varied regional performance within Land Mobility—with Japan showing strength while other key markets falter—emphasizes the necessity for highly localized and adaptable market strategies.
For Smart Power Vehicles, which include electrically power-assisted bicycles (eBikes), their drive units (e-Kits), and electric wheelchairs, unit sales increased compared to the previous year.5 However, despite this increase in units, revenue remained largely flat year-over-year due to a change in the model mix, suggesting a shift towards lower-priced or lower-margin models within this segment.5 The operating loss in this area was notably small, attributed to a decrease in SG&A expenses.5 Yamaha’s acquisition of the eBike drive unit business subsidiary from German automotive parts manufacturer Brose in March 2025 is a strategic move to bolster its presence in the European market and enhance its electronic control technologies.14 This indicates a long-term commitment to the growing electric mobility sector, even as the company navigates current margin pressures within the segment.
B. Marine Products Business
The Marine Products segment recorded revenues of ¥280.0 billion (approximately $1.89 billion USD), a 5.9% decrease year-over-year. Operating income for this segment fell by 26.5% to ¥38.9 billion (approximately $263 million USD).3
Demand for outboard motors in the crucial U.S. market was lower than anticipated, as were sales in Asia and other regions.3 Despite this, overall unit sales for outboard motors were on par with the previous year. This was primarily due to a surge in demand prior to the implementation of price changes in the U.S., particularly for small and midrange outboard models.3 This “pull-forward” of demand, where customers purchased products in anticipation of future price increases, suggests that the underlying market demand in the U.S. might be weaker than the reported unit sales initially indicate. This effect is likely to create a more pronounced headwind for outboard motor sales in the second half of 2025 as this pre-buying subsides and potentially higher prices deter new purchases. Yamaha maintains a strong market position, leading global outboard motor production with a 42% market share in 2025.15
Personal watercraft (PWC) experienced a clear decrease in demand in the main U.S. market, leading to a year-on-year decline in unit sales.3 The combined effect of lower PWC unit sales, higher procurement expenses, increased R&D expenses, and elevated labor and other SG&A expenses led to the overall decrease in profits for the Marine Products business.3
C. Outdoor Land Vehicle Business
The Outdoor Land Vehicle segment, which includes ATVs, recreational off-highway vehicles (ROVs), and golf cars, saw its revenues fall by 18.0% to ¥77.7 billion (approximately $525 million USD).3 This segment recorded an operating loss of ¥13.7 billion (approximately $93 million USD), a deepening from the slight loss reported in the previous year.3
Market demand for recreational vehicles (ATVs and ROVs) was below last year’s figures.10 While ATV sales remained robust, demand for side-by-side ROVs declined.3 Golf car sales were also lower, particularly in the U.S., with the company attributing this to weaker demand and rising SG&A costs.3 The overall reduction in revenue and the deepening operating loss for this segment, coupled with a “worsening model mix” in recreational vehicles, suggest a potential shift in consumer preferences or market saturation in certain categories.10 This indicates a need for product diversification or a re-evaluation of market strategies for ROVs and golf cars. Yamaha’s recent launch of new five-seater electric golf cars with in-house battery technology represents a strategic response to evolving market demands.1
D. Robotics Business
In stark contrast to other segments, the Robotics business emerged as a significant bright spot. Revenues for this segment increased by a robust 27.3% year-over-year to ¥24.4 billion.10 Furthermore, the operating loss for the Robotics segment significantly improved, narrowing to ¥1.4 billion from a loss of ¥3.7 billion in the prior year.10
This growth was primarily driven by higher demand in China and other Asian markets for the surface mounter segment.10 Critically, demand for generative AI applications and advanced packaging continues to grow, yielding higher sales of Yamaha’s semiconductor back-end process manufacturing equipment.10 This substantial revenue growth and reduced operating loss demonstrate Yamaha’s successful diversification into high-growth, technology-driven industrial sectors. The performance of this segment highlights that Yamaha is effectively leveraging its precision manufacturing and automation expertise to tap into secular trends beyond its traditional powersports markets. This strategic pivot provides a crucial counterbalance to the cyclicality and demand challenges faced by its core businesses, offering a pathway for future, more stable revenue streams and potentially higher margins. The continued investment in R&D for this area, which includes industrial robots, SMT equipment, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and industrial-use unmanned helicopters and drones, is clearly yielding positive results.14
E. Financial Services Business
The Financial Services business reported revenues of ¥27.8 billion, an increase of 3.3% year-over-year. However, operating income for this segment decreased by 33.8% to ¥4.1 billion.10
The increase in financial receivables contributed to the rise in revenues. The decline in operating income, despite revenue growth, points to the sensitivity of this segment to interest rate movements and financial market conditions. Specifically, appraised gains derived from interest rate swaps in the same period last fiscal year converted to appraisal losses this fiscal year, directly impacting profitability.10 This illustrates how changes in the broader financial environment, rather than operational efficiency, can significantly influence the segment’s performance.
F. Other Products Business
The Other Products business segment recorded revenues of ¥4.1 billion, a decrease of 19.9% year-over-year. This segment also saw its operating loss widen to ¥2.4 billion, up from a loss of ¥1.1 billion in the previous year.10 This declining revenue and increased operating loss indicate that this segment is currently a drag on overall profitability, suggesting that some of Yamaha’s smaller or newer ventures within this category are struggling to achieve profitability or scale.
Table 2: Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. Segmental Revenue and Operating Income/Loss (H1 2025)
| Segment | H1 2025 Revenue (¥ Billion) | H1 2025 Revenue (USD Million/Billion) | YoY Revenue Change (%) | H1 2025 Operating Income/Loss (¥ Billion) | H1 2025 Operating Income/Loss (USD Million) | YoY Operating Income/Loss Change (%) |
| Land Mobility | 808.2 | $5.46 Billion | -4.2% | 59.4 | $401 Million | -39.0% |
| Marine Products | 280.0 | $1.89 Billion | -5.9% | 38.9 | $263 Million | -26.5% |
| Outdoor Land Vehicle | 77.7 | $525 Million | -18.0% | (13.7) | ($93 Million) | Deeper Loss |
| Robotics | 24.4 | N/A | +27.3% | (1.4) | N/A | Reduced Loss |
| Financial Services | 27.8 | N/A | +3.3% | 4.1 | N/A | -33.8% |
| Other Products | 4.1 | N/A | -19.9% | (2.4) | N/A | Increased Loss |
Note: USD conversions are approximate based on average exchange rates for H1 2025 where $1 = ¥148 and €1 = ¥162. Some USD figures are directly provided by sources.
V. Key Factors Influencing H1 2025 Results
The decline in Yamaha Motor’s first-half performance was a confluence of several interconnected factors, ranging from shifts in market demand and operational challenges to rising costs and broader geopolitical influences.
Market Demand Shifts and Economic Headwinds
A significant contributor to the revenue decline was the weakening market demand across several of Yamaha’s core product categories. Motorcycles experienced declining unit sales in developed markets such as Europe and the U.S..3 Similarly, the Marine Products segment faced lower demand for both personal watercraft and outboard motors in the crucial U.S. market.3 The Outdoor Land Vehicle segment also saw weakened demand for golf cars in the U.S..3 These trends collectively point to an overall “demand lag” across key powersports categories, indicating a broader cooling of consumer spending in these discretionary product areas.3
Operational Challenges: Production Halts and Supply Chain Pressures
Beyond market demand, Yamaha faced specific operational hurdles that impacted its ability to meet sales targets. A notable issue was the temporary suspension of motorcycle production and shipments in Vietnam during the first quarter due to defective engine stamping.1 This internal quality control issue directly disrupted supply chains and sales in a key emerging market. Additionally, motorcycle unit sales in other significant emerging markets like India and Brazil also experienced declines.5 Across various businesses, higher procurement expenses contributed to increased costs, putting pressure on margins.3
Cost Structure Analysis: R&D, Procurement, Labor, and SG&A Expenses
The erosion of profitability was significantly influenced by an increase in the company’s cost base. Higher R&D expenses were consistently cited as a major factor in the profit decline across core businesses, including motorcycles and marine products.1 While these increased R&D expenses directly impact current profitability, they also represent a conscious strategic investment in future technologies. This suggests that a portion of the profit decline is a deliberate trade-off for long-term competitiveness and innovation, rather than solely a symptom of uncontrolled costs. This strategic investment is crucial for future growth and market relevance, particularly in areas like electric mobility and industrial automation.
In addition to R&D, higher labor costs and other SG&A expenses further contributed to reduced profits across segments.1 These cost pressures, stemming from a combination of general inflation and strategic investments, collectively masked the underlying efforts to strengthen the company’s future position.
Geopolitical and Regulatory Impacts: Tariffs and Local Taxation
External, non-operational factors also played a significant role in Yamaha’s financial performance. Increased U.S. tariffs were identified as impacting profitability.3 Furthermore, higher automobile taxes in Indonesia negatively affected demand in that market.1 The company also noted the potential for deferred tax asset reversals as a factor influencing its outlook.9 These macroeconomic and geopolitical headwinds are largely beyond the company’s direct control, creating a more volatile and unpredictable operating environment that necessitates agile global supply chain and pricing strategies. Their explicit mention as factors for the downward forecast revision underscores their increasingly significant impact on Yamaha’s financial health.
VI. Strategic Responses and Market Share Dynamics
Despite the pervasive challenges, Yamaha Motor demonstrated strategic agility and competitive resilience in several areas, indicating a proactive approach to navigating the difficult market landscape.
Areas of Market Share Gain: Identifying Strengths Amidst Challenges
Amidst overall unit sales declines, Yamaha successfully gained market share in some key areas, particularly within its core motorcycle and marine product businesses.5 This ability to expand market presence during a downturn is a strong indicator of competitive resilience and effective strategic execution. For instance, motorcycle sales in Japan increased, helping to stabilize revenue in that region.5 In the Marine Products segment, Yamaha maintains a dominant position, leading global outboard motor production with a 42% market share in 2025.15 While the U.S. market for outboard motors saw lower underlying demand, a rush of demand prior to price changes helped unit sales remain on par, suggesting that Yamaha was able to capture available demand effectively.3
The Robotics business also showcased significant strength, with increased unit sales overall, particularly driven by higher demand in China and other Asian markets.10 Even within the Outdoor Land Vehicle segment, ATV sales remained strong despite a decline in ROV sales, highlighting a resilient product line within a struggling category.3 This targeted resilience suggests that Yamaha is either outperforming weaker competitors in challenging markets or successfully capitalizing on specific demand pockets. This is a critical positive signal, as it positions the company to rebound more strongly when overall market conditions improve, having solidified or expanded its competitive footprint during a period of contraction. It also validates the company’s emphasis on a “long-term growth mindset” and “steady product investments”.3
Research and Development (R&D) Initiatives
Yamaha’s R&D strategy is notably diversified and forward-looking, with significant investments aimed at future-proofing the business and exploring new growth avenues. While these investments contribute to higher current R&D expenses, they are crucial for long-term competitiveness.
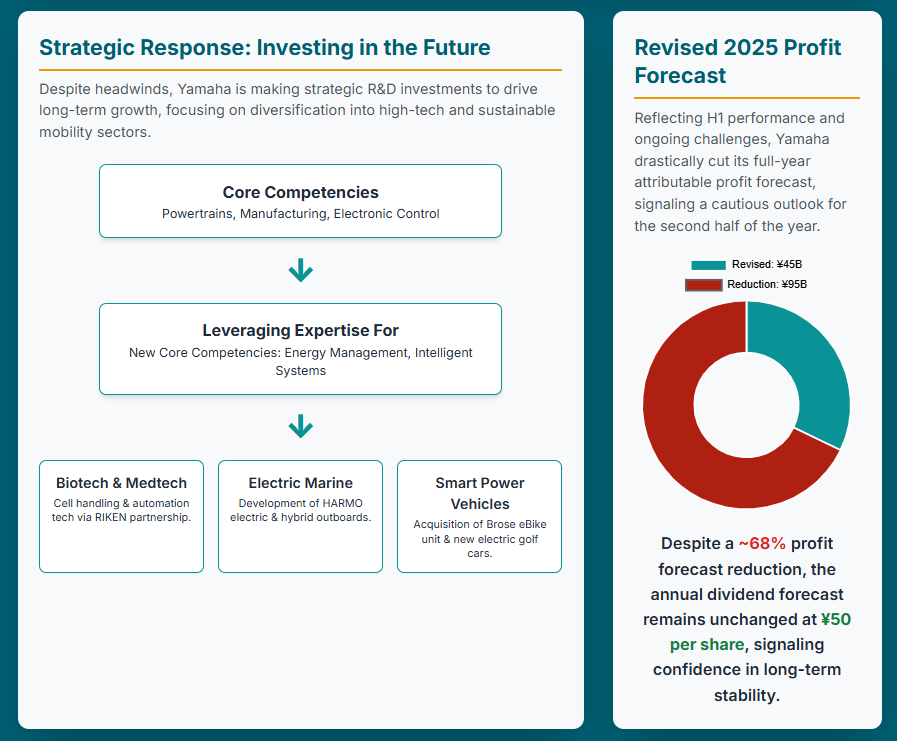
The company announced a joint research agreement with RIKEN, a national research and development agency, starting in July 2025 and running through March 2027.13 This collaboration focuses on next-generation cell handling and automation technologies, with the goal of promoting digital transformation (DX) and AI transformation (AX) in research settings. This initiative represents a significant strategic pivot into biotech and medtech, leveraging Yamaha’s expertise in precision robotics to diversify revenue streams beyond traditional manufacturing into potentially high-growth, high-margin sectors.13
In its core marine products, Yamaha continues to make ongoing investments in product development.3 This includes the development of electric and hybrid technologies for outboard motors, such as the HARMO electric outboards.15 These efforts address the global shift towards sustainability and electric mobility, aligning with evolving market demands and regulatory landscapes. Similarly, in the Land Mobility segment, the acquisition of German automotive parts manufacturer Brose’s eBike drive unit business in March 2025 is designed to bolster Yamaha’s presence in the European eBike market and enhance its electronic control technologies.14 The company also launched new five-seater electric golf cars with new in-house battery technology, further expanding its electric product portfolio.1
These strategic R&D outlays, while pressuring current profits, are critical for securing long-term growth, mitigating reliance on cyclical powersports markets, and maintaining technological leadership. The focus on new core competencies such as Energy Management, Intelligent Systems, and Software Services, alongside existing strengths in Powertrains, Electronic Control, Manufacturing, and Chassis/Hulls, demonstrates a comprehensive approach to future growth.14
Cost Control and Profitability Improvement Measures
In response to the challenging financial results, Yamaha Motor is actively implementing company-wide measures to improve profitability. These include rigorous cost controls, strategic pricing adjustments, and flexible production adjustments designed to align with demand trends and inventory levels, particularly to minimize the impact of tariffs.10 Management is focused on making rapid efforts to improve the profit structure 5 and is working to optimize production layouts and procurement processes.17 These initiatives underscore a commitment to operational efficiency and financial discipline in a difficult economic climate.
Product Portfolio and Pricing Strategies
The company’s approach to its product portfolio and pricing is evident in several areas. The rush of demand for small and midrange outboard models in the U.S. prior to price changes indicates a tactical use of pricing to stimulate sales.3 Looking ahead, motorcycle supply is expected to improve in the second half of the year as production in Vietnam resumes.3 Furthermore, in the Outdoor Land Vehicle segment, there is an emphasis on focusing on ATV sales to offset the softness observed in side-by-side (ROV) demand.3 These strategies aim to adapt to current market conditions and leverage existing product strengths.
VII. Full-Year 2025 Outlook and Management Commentary
Yamaha Motor’s first-half performance led to a significant downward revision of its full-year 2025 financial forecasts, reflecting a more cautious and realistic outlook for the remainder of the fiscal year.
Revised Consolidated Forecasts: Revenue, Operating Income, and Net Income
The initial forecast for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2025, announced on February 12, 2025, projected robust figures: revenue of ¥2,700.0 billion, operating income of ¥230.0 billion, and net income of ¥140.0 billion, with an EPS of ¥143.21.10 However, following the H1 2025 results, the company dramatically cut its full-year projections. The revised forecast now anticipates revenue of ¥2,570 billion (approximately $16.6 billion USD), a slight decrease of 0.2% year-over-year.7 The most substantial revision is to attributable profit (net income), which is now projected at ¥45.0 billion, a drastic ~68% reduction from the initial ¥140.0 billion expected.9 Consequently, the basic EPS forecast has been slashed to ¥46.34 from the original ¥143.21.9
This substantial downward revision of the full-year net profit forecast is a stark acknowledgment from management that the challenges faced in the first half are not merely temporary but are expected to persist and potentially intensify. This indicates that the company anticipates continued pressure from lower sales volumes, higher operational costs (including tariffs and taxes), and potentially other unforeseen issues such as deferred tax asset reversals.9 This revised outlook suggests a more challenging second half than initially projected, necessitating robust cost management and strategic agility to mitigate further impacts. It also implies that while the market share gains in certain areas are positive, they are not sufficient to fully offset the broader economic and operational headwinds impacting overall profitability.
Analysis of Factors Driving Downward Revisions
The revised outlook is primarily driven by a continuation of the factors that impacted the first half. These include ongoing sales challenges in key product lines and markets, particularly in motorcycles and marine products.3 The impact of increased U.S. tariffs is expected to continue affecting profitability, as are higher automobile taxes in Indonesia, which are projected to suppress demand.1 Furthermore, inflation in labor and development costs is expected to persist, adding to the cost pressures.3 The potential for deferred tax asset reversals also contributes to the more conservative profit forecast.9
Management’s Strategic Priorities for H2 2025 and Beyond
In response to these challenges, Yamaha’s management has outlined clear strategic priorities. President and CEO Motofumi Shitara emphasized the company’s commitment to implementing thorough cost controls and accelerating efforts to improve its profit structure as quickly as possible.3 The company plans to continue selecting areas for focused action and concentration, aiming to build a more resilient organization and maximize corporate value over the long term.3 Specific operational improvements are also anticipated, with motorcycle supply expected to improve in the second half as production in Vietnam resumes.3
Dividend Policy and Shareholder Returns
Despite the significant cut to its profit forecast, Yamaha Motor has maintained its total annual dividend forecast of ¥50 per share for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2025.5 The company expects to pay a year-end dividend of ¥25.00 per share.9 Maintaining the dividend forecast amidst a drastic reduction in net profit signals management’s commitment to shareholder returns, even in a challenging environment. This decision could be viewed positively by investors seeking stability, as it suggests a confidence in future cash flow generation or a strategic decision to prioritize shareholder confidence over strict payout ratio adherence in the short term.
Table 3: Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. Full-Year 2025 Forecast Comparison
| Metric | Initial Forecast (Feb 12, 2025) | Revised Forecast (H1 2025) | Percentage Change |
| Revenue | ¥2,700.0 Billion | ¥2,570 Billion | -4.8% |
| Operating Income | ¥230.0 Billion | N/A | N/A |
| Attributable Profit | ¥140.0 Billion | ¥45.0 Billion | -67.9% |
| Basic EPS | ¥143.21 | ¥46.34 | -67.7% |
Note: The revised forecast provided “Attributable Profit” instead of “Net Income” directly, but it refers to the same bottom-line profit metric.
VIII. Analyst and Market Sentiment
The financial community’s perception of Yamaha Motor’s performance and future prospects reflects a nuanced understanding of the current challenges versus the company’s long-term strategic positioning.
Stock Performance and Recent Trends
Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. (TYO:7272) stock has experienced some volatility around its earnings announcements. For instance, the stock price fell by 0.102% on August 6, 2025, continuing a three-day decline.20 Over the past year, the stock has underperformed relative to both the Japanese Auto industry and the broader Japanese Market, which returned 3.2% and 16.1% respectively.18 This underperformance indicates investor caution in light of the declining financial results and revised outlook. The stock’s weekly volatility has remained stable over the past year, suggesting that while it experiences price movements, they have not been excessively erratic.18
Consensus Analyst Ratings and Price Targets
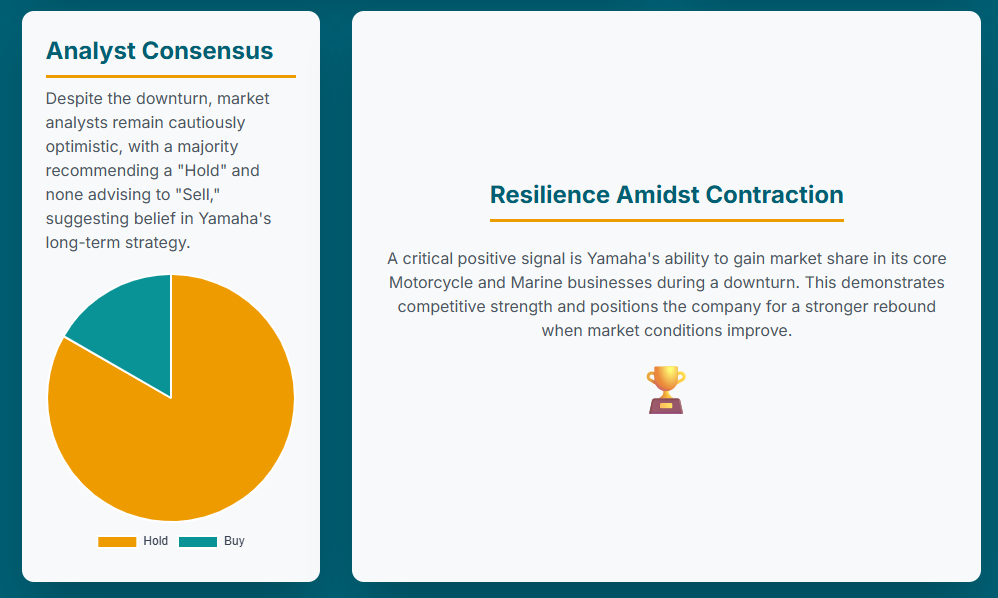
Despite the recent financial downturn, analyst sentiment towards Yamaha Motor remains largely positive or neutral. As of June 30, 2025, based on ratings from 12 analysts, Yamaha Motor received 16.67% Buy ratings and 83.33% Hold ratings, with no Sell ratings.21 The average analyst price target for the next 12 months is ¥1,140.00, with a maximum estimate of ¥1,300.00 and a minimum estimate of ¥1,000.00.21 Other sources indicate similar average targets, such as ¥1,192.44 22 or ¥1,120.0.16
The prevailing “Buy” and “Hold” ratings, coupled with price targets generally above current stock levels, suggest that analysts believe Yamaha’s current challenges are either temporary or that the company’s long-term strategic initiatives and market positioning will eventually drive recovery and value creation. This perspective likely factors in the strategic R&D investments in areas like cell handling technology and electric/hybrid products 13, the demonstrated ability to gain market share in core areas 5, and the company’s stated commitment to building a “resilient company”.3 This longer-term view contrasts with the immediate negative financial results, highlighting a potential opportunity for investors who share this long-term outlook and can look beyond the short-term headwinds.
Table 4: Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. Analyst Consensus and Price Targets (as of June 30, 2025)
| Rating Category | Percentage of Analysts | Number of Analysts |
| Strong Buy | 0.00% | 0 |
| Buy | 16.67% | 2 |
| Hold | 83.33% | 10 |
| Underperform | 0.00% | 0 |
| Sell | 0.00% | 0 |
| Metric | Value (¥) |
| Average Price Target | 1,140.00 |
| Minimum Estimate | 1,000.00 |
| Maximum Estimate | 1,300.00 |
Source: Based on 12 analysts.21
Key Concerns and Opportunities from an Investor Perspective
From an investor standpoint, several concerns arise from the H1 2025 results. The company’s debt is not well covered by operating cash flow, profit margins are significantly lower than the previous year, and the dividend coverage by free cash flows is not strong.18 These factors indicate potential financial strain and could raise questions about the sustainability of current operations if the downturn persists.
However, opportunities for long-term value creation are also present. The company’s strategic focus on the expansion of premium models, digital services, and continued investments in its marine segment position Yamaha for potentially higher margins and further market share gains, which could lead to stronger global leadership beyond current analyst forecasts.18 Analysts also forecast Yamaha’s earnings to grow by 20.3% per year, which is above the savings rate and faster than the U.S. market, suggesting a positive outlook for future profitability.23 This requires investors to balance the immediate financial pressures and operational challenges against Yamaha’s long-term strategic investments and its demonstrated capacity to gain market share in key areas. The company’s “long-term growth mindset” 3 is a crucial element for attracting and retaining patient capital that can look beyond the current headwinds.
IX. Conclusion and Forward-Looking Perspectives
The first half of fiscal year 2025 proved to be a challenging period for Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd., characterized by a notable decline in revenue and a disproportionately severe erosion of profitability. This margin compression highlights that the company’s challenges extend beyond mere sales volume reductions to encompass significant cost pressures from higher R&D, procurement, labor, and SG&A expenses, compounded by external factors such as U.S. tariffs and Indonesian taxes. Operational disruptions, particularly the temporary suspension of motorcycle production in Vietnam, further exacerbated these issues.
Despite these headwinds, Yamaha demonstrated pockets of resilience and strategic foresight. The company managed to gain market share in specific core segments, including motorcycles in Japan and the robust Robotics business in Asia. This ability to consolidate or expand market presence during a downturn underscores underlying competitive strength and the effectiveness of localized strategies in certain areas. Furthermore, Yamaha’s sustained and diversified R&D investments, particularly in advanced areas like cell handling technology, electric/hybrid marine products, and eBikes, signal a clear commitment to future-proofing the business and exploring high-growth, less cyclical sectors. These strategic outlays, while impacting current profits, are vital for securing long-term growth and maintaining technological leadership.
The substantial downward revision of the full-year 2025 profit forecast is a stark acknowledgment from management that the challenges are expected to persist, necessitating robust cost management and strategic agility. However, the decision to maintain the dividend forecast, even amidst this profit decline, suggests a commitment to shareholder returns and a degree of confidence in future cash flow generation.
Strategic Implications for Yamaha Motor’s Future Trajectory
The H1 2025 results underscore the increasing importance of strategic diversification beyond traditional powersports into higher-growth, less cyclical sectors like robotics and advanced mobility. The company’s commitment to R&D, even at the expense of short-term profits, indicates a strategic pivot towards capturing emerging market opportunities and enhancing its technological capabilities. The ability to gain market share in challenging conditions suggests an underlying competitive strength and the potential for a stronger rebound when market conditions improve.
Opportunities for Growth and Mitigation of Risks
Looking ahead, significant opportunities for growth exist in the Robotics segment, driven by the expanding demand for AI applications and advanced packaging. The company’s continued investment and expansion in electric mobility, including eBikes, electric golf cars, and HARMO electric outboards, position it well to capitalize on the global shift towards sustainable transportation. A potential recovery in motorcycle sales in the second half of the year, as production in Vietnam normalizes, could also provide some uplift.
To mitigate ongoing risks, Yamaha must continue to prioritize rigorous cost controls and efficiency improvements across all operations. Flexible production and pricing strategies will be crucial to counter the impacts of tariffs and dynamic demand shifts. Strategic investments in high-growth areas should be sustained to offset the cyclicality inherent in traditional powersports markets.
Recommendations for Stakeholders
For investors, it is advisable to consider Yamaha’s long-term strategic vision and R&D investments as key drivers of future value, balancing them against the current profitability challenges and external headwinds. Monitoring the effective execution of cost control measures and the performance of growth segments like Robotics and eBikes will be critical indicators of the company’s ability to navigate the current environment.
For management, resolving operational bottlenecks, such as the quality issues that led to production suspensions in Vietnam, should be a top priority to ensure consistent supply. Continued aggressive cost management is essential, but it must be balanced with strategic investment in R&D for long-term competitive advantage. Adapting product offerings and marketing strategies to address diverse regional demands and evolving consumer preferences—such as the demand for electric scooters in India or the shift from ROVs to ATVs—will be crucial for maintaining and expanding market presence.
The first half of 2025 represents a critical test for Yamaha Motor. The significant profit decline, coupled with external pressures, demands strong leadership and agile execution. However, the underlying strategic investments in R&D and the demonstrated ability to gain market share in specific areas suggest that Yamaha is not merely reacting to headwinds but is actively shaping its future. The coming quarters will reveal the effectiveness of these strategic pivots and the company’s resilience in navigating a complex global economic landscape. While the short-term outlook is challenging, Yamaha’s long-term strategic direction and underlying competitive strengths offer a basis for cautious optimism regarding its future trajectory.
Sources
- Yamaha Motor: Consolidated Business Results Summary – First Half …, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250805154633/en/Yamaha-Motor-Consolidated-Business-Results-Summary—First-Half-of-Fiscal-Year-Ending-December-31-2025–
- Yamaha Motor: Consolidated Business Results Summary – First Half of Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2025 – | Morningstar, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.morningstar.com/news/business-wire/20250805154633/yamaha-motor-consolidated-business-results-summary-first-half-of-fiscal-year-ending-december-31-2025
- Yamaha reports ‘demand lag’ for powersports and marine segments in Q2, accessed August 8, 2025, https://powersportsbusiness.com/news/yamaha/2025/08/06/yamaha-reports-demand-lag-for-powersports-and-marine-segments-in-q2/
- Yamaha Motor: Consolidated Business Results Summary – First Half of Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2025 – STT Info, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.sttinfo.fi/tiedote/71337515/yamaha-motor-consolidated-business-results-summary-first-half-of-fiscal-year-ending-december-31-2025?publisherId=58763726&lang=en
- Consolidated Business Results Summary- First Half of Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2025 – – News releases | Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd., accessed August 8, 2025, https://global.yamaha-motor.com/news/2025/0805/result.html
- Yamaha Motor: Consolidated Business Results Summary – First Half of Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2025 – | Financial Post, accessed August 8, 2025, https://financialpost.com/pmn/business-wire-news-releases-pmn/yamaha-motor-consolidated-business-results-summary-first-half-of-fiscal-year-ending-december-31-2025
- Yamaha Releases First Half 2025 Results – Trade Only Today, accessed August 8, 2025, https://tradeonlytoday.com/industry-news/yamaha-releases-first-half-2025-results/
- Yamaha Motor H1 Profit, Revenue Decline – Finanznachrichten, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.finanznachrichten.de/nachrichten-2025-08/66085417-yamaha-motor-h1-profit-revenue-decline-020.htm
- Yamaha Motor Profit Plunges 53% in H1, Cuts Forecast Due to Production Halts and US Tariff Impact – Moomoo, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.moomoo.com/news/post/56436392/yamaha-motor-profit-plunges-53-in-h1-cuts-forecast-due
- Consolidated Business Results Summary – First Three Months of the Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2025 – News releases | Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd., accessed August 8, 2025, https://global.yamaha-motor.com/news/2025/0513/result.html
- Yamaha 2025. First Half Two-Wheeler Global Sales Reached 2.3 Million – Motorcycles Data, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.motorcyclesdata.com/2025/08/01/yamaha-motorcycles/
- Yamaha Motor Hits The Brakes As Profits Fall Sharply – Finimize, accessed August 8, 2025, https://finimize.com/content/yamaha-motor-hits-the-brakes-as-profits-fall-sharply
- Yamaha Motor Begins Joint Research Using Cell Handling Technology with a national research institute – Advancing Next-Generation Automated Experimentation to Promote DX and AX in Research – – News releases, accessed August 8, 2025, https://global.yamaha-motor.com/news/2025/0807/ch2.html
- Integrated Report 2025 – Yamaha Motor Global, accessed August 8, 2025, https://global.yamaha-motor.com/ir/integrated-report/integrated2025/pdf/YMC_IR2025_Eng.pdf
- 2025 Trends: New Yamaha Outboard Motors Market Dominance – Accio, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.accio.com/business/trend-of-new-yamaha-outboard-motors
- Yamaha Motor Co Ltd Stock Price Today | TYO: 7272 Live – Investing.com, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.investing.com/equities/yamaha-motor-co-ltd
- Earnings Presentation – Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd., accessed August 8, 2025, https://global.yamaha-motor.com/ir/library/report/pdf/2025/2025explain-q1-e.pdf
- Yamaha Motor (TSE:7272) – Stock Analysis – Simply Wall St, accessed August 8, 2025, https://simplywall.st/stocks/jp/automobiles/tse-7272/yamaha-motor-shares
- Business Results for the First Three Months of the Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2025 – Yamaha Motor Global, accessed August 8, 2025, https://global.yamaha-motor.com/ir/library/report/pdf/2025/2025report-q1-e.pdf
- Yamaha Stock Price Forecast. Should You Buy 7951.T? – StockInvest.us, accessed August 8, 2025, https://stockinvest.us/stock/7951.T
- Yamaha Motor (7272) Stock Forecast & Analyst Ratings – 富途牛牛, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.futunn.com/en/stock/7272-JP/forecast
- www.tipranks.com, accessed August 8, 2025, https://www.tipranks.com/stocks/jp:7272/forecast#:~:text=7272%20Analyst%20Recommendation%20Trends&text=In%20the%20current%20month%2C%207272,past%203%20months%20is%201%2C192.44.
- Yamaha (OTCPK:YAMC.Y) Stock Forecast & Analyst Predictions – Simply Wall St, accessed August 8, 2025, https://simplywall.st/stocks/us/consumer-durables/otc-yamc.y/yamaha/future
Our Social Media Handles
- Instagram : LivingWithGravity
- Medium : Akash Dolas
- YouTube Channel : Gear and Shutter



































