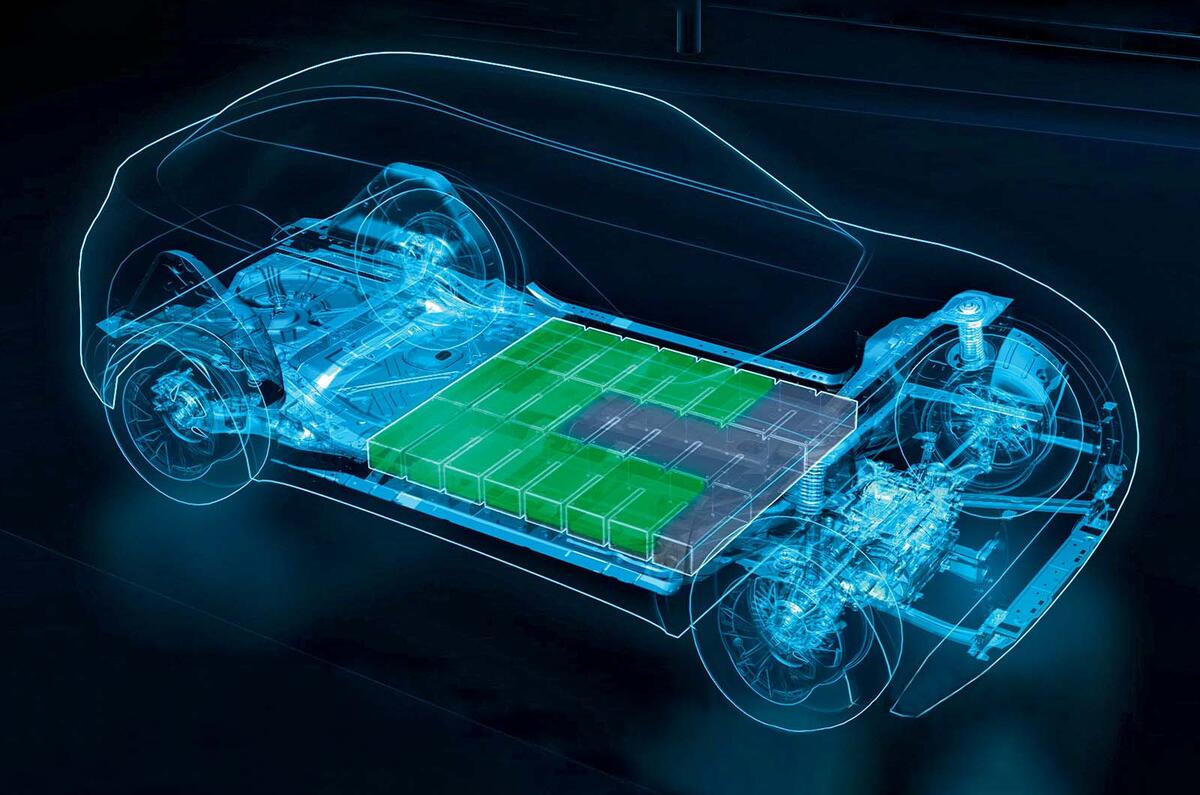
The Intelligent Battery Integrated System (Ibis) is indeed an innovative approach to simplify EV powertrains. Decentralizing the conversion process with microinverters embedded in each battery module streamlines the power distribution setup, potentially saving costs, weight, and space.
The Ibis project is an interesting idea to reduce the number of components in an EV powertrain. It does this by integrating the charger and inverter into each battery module. This could potentially make EVs smaller and cheaper, and it could also improve efficiency. However, it is still in the early stages of development, so it is not yet clear if it will be successful.
Let’s explore the potential implications and challenges of this approach:
1. Benefits:
Simplification: Fewer primary components could lead to easier design, installation, and maintenance.
Space Saving: In small EVs where every inch matters, the combined battery module, charger, and microinverter could save significant space.
Cost Reduction: High-voltage components tend to be more expensive. If multiple smaller, low-voltage components can be produced at a lower cost than their high-voltage counterparts, there would be a financial advantage.
Modularity: If one module fails, only that module needs replacement, potentially making servicing more straightforward.
2. Potential Challenges:
Heat Management: Microinverters generate heat. With the embedded battery modules, managing the generated heat will be crucial. Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and excessive heat can degrade their performance and lifespan.
Reliability: With numerous microinverters, the chance of individual component failure could increase compared to a single, centralized inverter.
Standardization: One of the challenges in EV manufacturing is creating standardized systems that can be scaled efficiently. Introducing microinverters in each battery module could complicate standardization efforts.
Compatibility with other concepts: As pointed out, other automotive players are exploring unique strategies. Volkswagen, for instance, is considering integrating individual battery cells directly into the car’s chassis. Ibis might not align with such approaches.
Conclusion
In essence, while the Ibis project offers a promising direction in streamlining EV powertrains, real-world testing and commercial viability assessments will determine its success. The balance between benefits like cost-saving and simplification against challenges like heat management and compatibility will play a decisive role.